最近距离问题
在这个例子中, 我们演示了如何在OPTIMake的框架下构建并求解通用优化问题, 即stage数为1的问题.
当stage数设置为1时, OPTIMake的建模接口退化为:
信息
- 上述优化问题为通用的优化问题形式, 其中目标函数, 等式约束, 不等式约束分别通过建模接口函数
objective,start_equality,inequality定义 - stage数为1时, 涉及到多stage的建模接口函数不可调用:
end_objective,end_equality,equality
注意
OPTIMake并不是针对大规模通用优化问题的求解所设计. 当满足以下条件时, OPTIMake能实现对通用优化问题 (stage数为1问题)的高效建模与求解:
- 变量/约束维度小于100
- 具备固定的维度与稀疏结构
问题描述
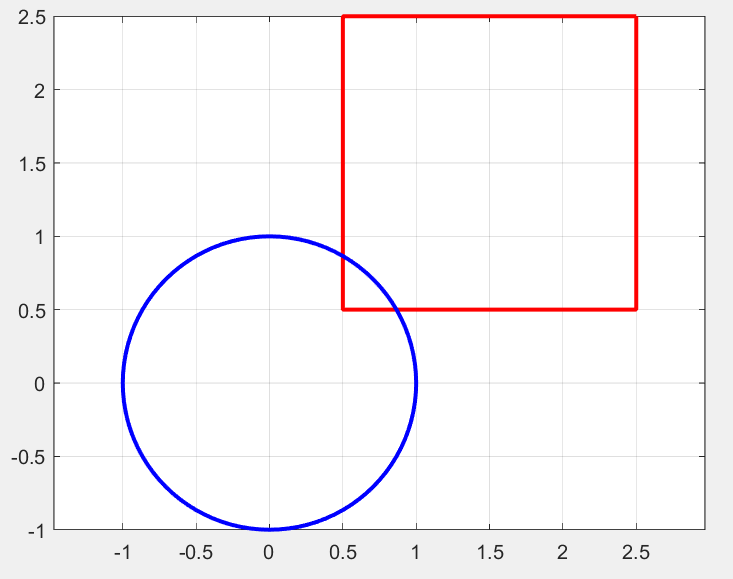
圆和矩形之间的最近距离 (圆与矩形相交时, 最近距离为0) 可以构建为优化问题求解.
设矩形的中心为 ,长宽分别为 , 圆心在原点,半径为 .
假设和分别为矩阵和圆内的点, 那么最近距离问题可以描述为最小化和之间的距离, 即
在圆内可以通过下面的二次约束描述:
在矩形内可以通过多种方式描述, 这里我们采用矩形的顶点来描述. 设矩形的四个顶点为. 那么矩阵内的点可以描述为4个顶点的加权平均, 即
建模
上述的优化问题在OPTIMake中的建模如下:
prob = multi_stage_problem('squared_distance', 1)
# rectangle parameters
# center: (x, y), rotation: phi
# length: l, width: w
l, w = prob.parameters(['l', 'w'], stage_dependent=False)
x, y, phi = prob.parameters(['x', 'y', 'phi'], stage_dependent=False)
# circle parameters
# center: (0, 0), radius: r
r = prob.parameters(['r'], stage_dependent=False)
# point inside the circle
xo = prob.variable('xo')
yo = prob.variable('yo')
theta1 = prob.variable('theta1', hard_lowerbound=0.0)
theta2 = prob.variable('theta2', hard_lowerbound=0.0)
theta3 = prob.variable('theta3', hard_lowerbound=0.0)
theta4 = prob.variable('theta4', hard_lowerbound=0.0)
# rectangle vertices
V = Matrix([[+l / 2.0, +w / 2.0],
[+l / 2.0, -w / 2.0],
[-l / 2.0, -w / 2.0],
[-l / 2.0, +w / 2.0]])
# rotation matrix
R = Matrix([[cos(phi), -sin(phi)],
[sin(phi), cos(phi)]])
# rotated rectangle vertices
V = V * R
theta = Matrix([theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4])
# point inside the rectangle
pos_rec = V.transpose() * theta + Matrix([[x], [y]])
xr, yr = pos_rec[0], pos_rec[1]
obj = general_objective((xr - xo)**2 + (yr - yo)**2)
prob.objective(obj)
seq = general_equality([theta1 + theta2 + theta3 + theta4 - 1.0])
prob.start_equality(seq)
ineq = general_inequality(
expr = [xo**2 + yo**2 - r**2],
sign = ['<='],
bound = [0.0])
prob.inequality(ineq)
option = codegen_option()
option.default_tolerance_level = 'high'
codegen = code_generator()
codegen.codegen(prob, option)
求解
#include "squared_distance_prob.h"
#include "squared_distance_solver.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
Squared_distance_Problem prob;
Squared_distance_Option option;
Squared_distance_WorkSpace ws;
Squared_distance_Output output;
squared_distance_init(&prob, &option, &ws);
/* params */
prob.param[SQUARED_DISTANCE_PARAM_X] = 2.0; /* x */
prob.param[SQUARED_DISTANCE_PARAM_Y] = 2.0; /* y */
prob.param[SQUARED_DISTANCE_PARAM_PHI] = 0.2; /* phi */
prob.param[SQUARED_DISTANCE_PARAM_L] = 4.0; /* l */
prob.param[SQUARED_DISTANCE_PARAM_W] = 2.0; /* w */
prob.param[SQUARED_DISTANCE_PARAM_R] = 1.0; /* r */
/* option */
option.print_level = 1;
int solve_status = squared_distance_solve(&prob, &option, &ws, &output);
printf("solve_status = %d\n", solve_status);
printf("squared distance = %f\n", output.obj);
printf("(xo, yo) = (%f, %f)\n", \
output.primal.var[0][SQUARED_DISTANCE_VAR_XO], output.primal.var[0][SQUARED_DISTANCE_VAR_YO]);
return 0;
}
结果
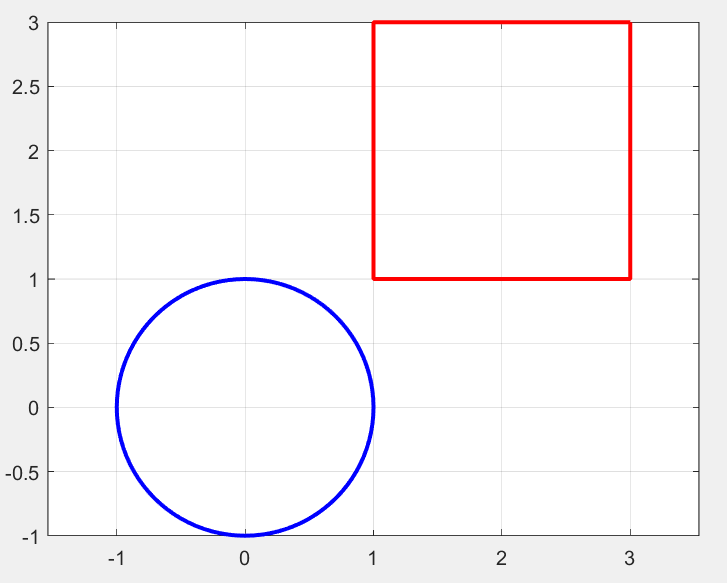
当 , , , , , 时, 计算的 (可通过output.obj获取):

当 , , , , , 时, 计算的:
当 , , , , , 时, 即圆与矩形相交时, 计算的: