Reusable Launch Vehicle Entry
Problem Description
Consider the following optimal control problem of maximizing the crossrange during the atmospheric entry of a reusable launch vehicle and taken verbatim from Ref [1]. Minimize the cost functional and subject to the dynamic constraints,
and the boundary conditions:
Further details of this problem, including the aerodynamic model, can be found in Ref. The code for solving this problem is shown below.
信息
对于飞行器而言, 气动系数一般是随着速度、高度等环境因素变化的, OPTIMake将有专门处理 LookupTable函数支持�这类输入, 并实现与求解器的高效集成.
Modeling
# --------------- Reusable Launch Vehicle Entry Example --------------- #
# This example is taken varbatim from the following reference: #
# Practial Methods for Optimal Control and Estimation Using Nonlinear #
# Programming. SIAM Press, Philadelphia, 2009 #
# --------------------------------------------------------------------- #
NN = 100
prob = multi_stage_problem('reentry', NN + 1)
cft2m = 0.3048 # cf to m
cft2km = cft2m / 1000 # cf to km
cslug2kg = 14.5939029
""" Provide Auxiliary Data for Problem """
Re = 6371203.92 # Equatorial Radius of Earth (m)
S = 249.9091776 # Vehicle Reference Area (mˆ2)
cl = [-0.2070, 1.6756] # Parameters for Lift Coefficient
cd = [0.0785, -0.3529, 2.0400] # Parameters for Drag Coefficient
b = [0.07854, -0.061592, 0.00621408] # Parameters for Heat Rate Model
al = [-0.20704, 0.029244] # Parameters for Heat Rate Model
rho0 = 1.225570827014494 # Sea Level Atmospheric Density (kg/mˆ3)
mu = 3.986031954093051e14 # Earth Gravitational Parameter (mˆ3/sˆ2)
mass = 92079.2525560557 # Vehicle Mass (kg)
""" Boundary Conditions """
rad0, lon0, lat0, speed0, fpa0, azi0 = prob.parameters(['rad0', 'lon0', 'lat0', 'speed0', 'fpa0', 'azi0'], stage_dependent=False)
radf, speedf, fpaf, azif = prob.parameters(['radf', 'speedf', 'fpaf', 'azif'], stage_dependent=False)
H = prob.parameters(['H'], stage_dependent=False)
# H = 7254.24 # Density Scale Height (m)
""" Limits on Variables """
tfMin, tfMax = 1.0, 3000.0
radMin, radMax = Re, rad0
lonMin, lonMax = -pi, pi
latMin, latMax = -70.0 * pi / 180.0, 70.0 * pi / 180.0
speedMin, speedMax = 10.0, 45000.0
fpaMin, fpaMax = -80.0 * pi / 180.0, 80.0 * pi / 180
aziMin, aziMax = -180.0 * pi / 180.0, 180.0 * pi / 180.0
aoaMin, aoaMax = -90.0 * pi / 180.0, 90.0 * pi / 180.0
bankMin, bankMax = -90.0 * pi / 180.0, 1.0 * pi / 180.0
rad = prob.variable('rad', hard_lowerbound=radMin, hard_upperbound=radMax)
lon = prob.variable('lon', hard_lowerbound=lonMin, hard_upperbound=lonMax)
lat = prob.variable('lat', hard_lowerbound=latMin, hard_upperbound=latMax)
v = prob.variable('v', hard_lowerbound=speedMin, hard_upperbound=speedMax)
fpa = prob.variable('fpa', hard_lowerbound=fpaMin, hard_upperbound=fpaMax)
azi = prob.variable('azi', hard_lowerbound=aziMin, hard_upperbound=aziMax)
tf = prob.variable('tf', hard_lowerbound=tfMin, hard_upperbound=tfMax)
bank = prob.variable('bank', hard_lowerbound=bankMin, hard_upperbound=bankMax) # bank
aoa = prob.variable('aoa', hard_lowerbound=aoaMin, hard_upperbound=aoaMax) # aoa
""" Compute the Aerodynamic Quantities """
cd0 = cd[0]
cd1 = cd[1]
cd2 = cd[2]
cl0 = cl[0]
cl1 = cl[1]
altitude = rad - Re
CD = cd0 + cd1 * aoa + cd2 * aoa ** 2
rho = rho0 * exp(-altitude / H)
CL = cl0 + cl1 * aoa # lift coefficient
q = 0.5 * rho * v ** 2
D = q * S * CD / mass
L = q * S * CL / mass
gravity = mu / (rad ** 2)
""" Evaluate Right-Hand Side of the Dynamics """
raddot = v * sin(fpa)
londot = v * cos(fpa) * sin(azi) / (rad * cos(lat))
latdot = v * cos(fpa) * cos(azi) / rad
vdot = -D - gravity * sin(fpa)
fpadot = (L * cos(bank) - cos(fpa) * (gravity - v ** 2 / rad)) / v
azidot = (L * sin(bank) / cos(fpa) + v ** 2 * cos(fpa) * sin(azi) * tan(lat) / rad) / v
dynamics = [raddot, londot, latdot, vdot, fpadot, azidot, 0]
ts = tf / NN
ode = differential_equation(
state=[rad, lon, lat, v, fpa, azi, tf],
state_dot=dynamics,
stepsize=ts,
discretization_method='trapezoid')
prob.equality(ode)
obj = general_objective(-lat)
# maximize range
prob.end_objective(obj)
seq = general_equality([rad - rad0, lon - lon0, lat - lat0, v - speed0, fpa - fpa0, azi - azi0])
prob.start_equality(seq)
eeq = general_equality([rad - radf, v - speedf, fpa - fpaf])
prob.end_equality(eeq)
option = codegen_option()
option.common_subexpression_elimination = 'off'
codegen = code_generator()
codegen.codegen(prob, option)
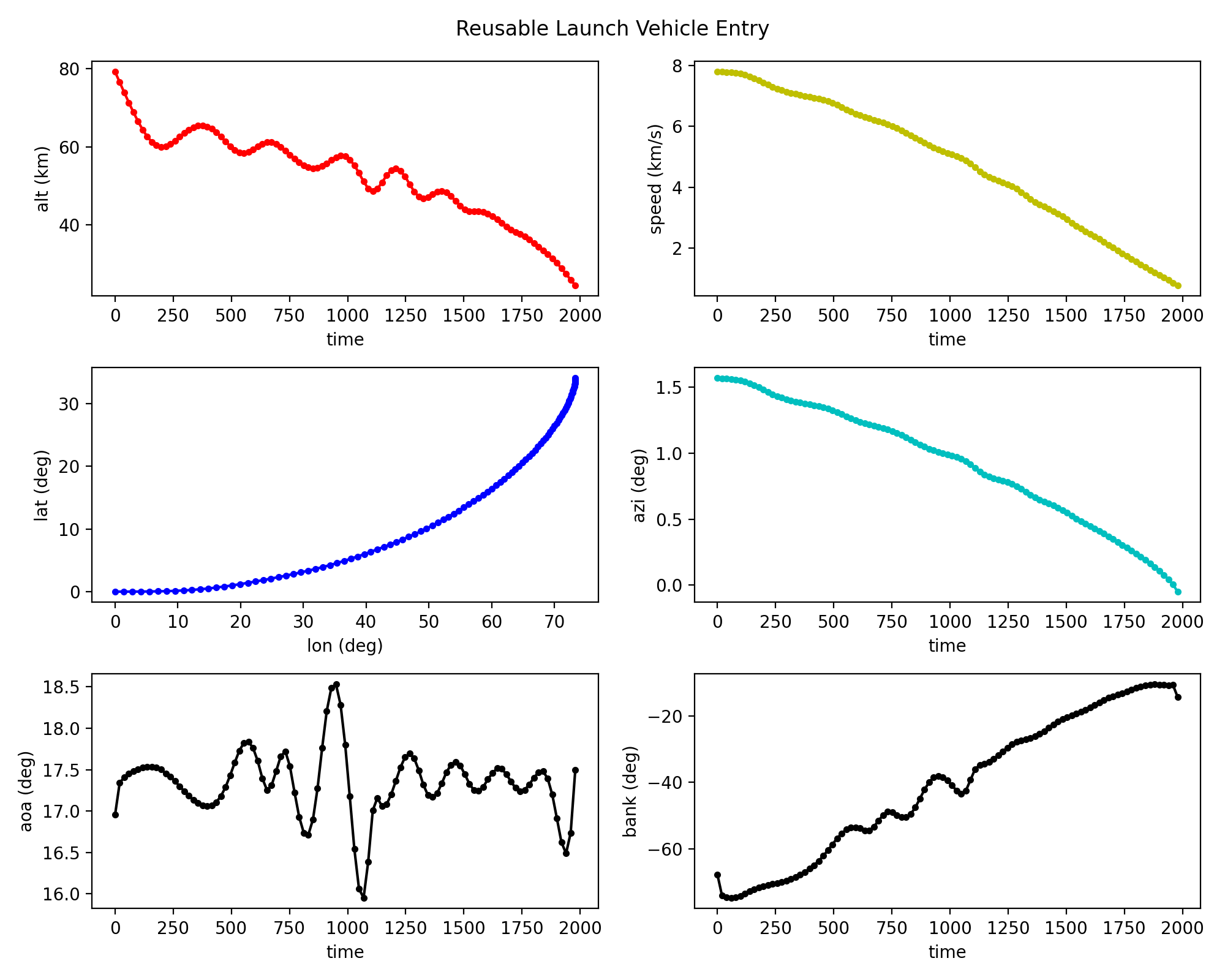
Solution
[1]. Betts, J. T., Practical Methods for Optimal Control and Estimation Using Nonlinear Programming, SIAM Press, Philadelphia, 2009.